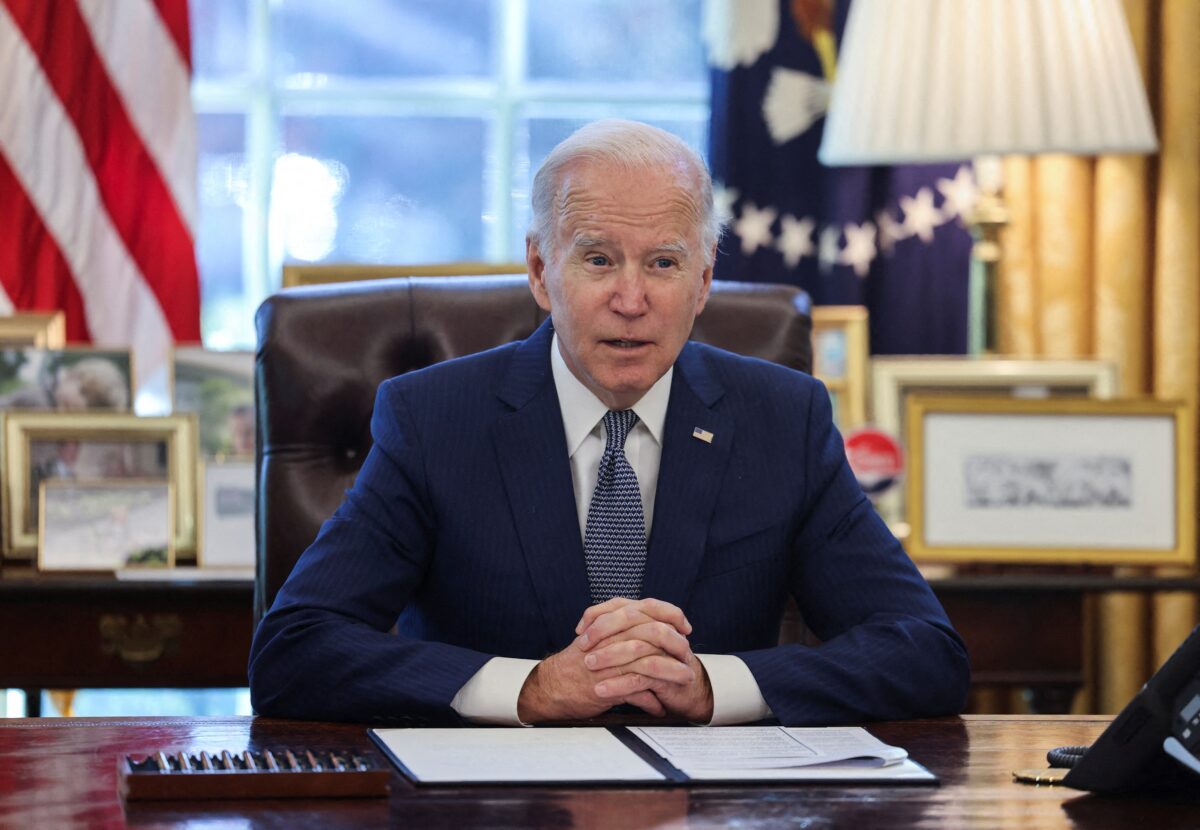
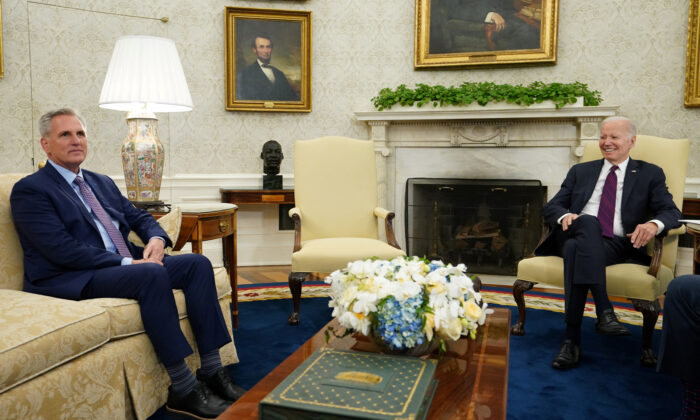
President Joe Biden signed the Fiscal Responsibility Act on Saturday, suspending the debt ceiling for 19 months and bringing a monthslong political battle to a close.
The compromise legislation negotiated by Biden and House Speaker Kevin McCarthy (R-Calif.) passed both houses of Congress with bipartisan support this week, averting a potential default on the nation’s financial obligations.
“Passing this budget agreement was critical. The stakes could not have been higher,” Biden said in a Friday evening address to the nation from the Oval Office.
Congressional leaders in both parties, eager to avoid financial disaster, endorsed the bill.
McCarthy referred to the legislation in historic terms, calling it the biggest spending cut ever enacted by Congress. Senate Majority Leader Chuck Schumer (D-N.Y.) said, “We’ve saved the country from the scourge of default,” after the bill passed the Senate on June 1.
House Minority Leader Hakeem Jeffries (D-N.Y.) and Senate Minority Leader Mitch McConnell (R-Ky.) both supported the bill.
Biden vs. McCarthy
The president’s signature ends a monthslong cold war with McCarthy over terms for raising the nation’s $31.4 trillion debt ceiling.
The Financial Responsibility Act suspends the debt ceiling until Jan. 1, 2025, cuts non-defense discretionary spending slightly in 2024, and limits discretionary spending growth to 1 percent in 2025.
The agreement also contains permitting reforms for oil and gas drilling, changes to work requirements for some social welfare programs, and clawbacks of $20 billion in IRS funding and $30 billion in unspent COVID-19 relief funds, among other provisions.
In the absence of congressional action to allow additional borrowing, the United States would have lacked the ready cash to pay all of its bills on June 5, according to Treasury Secretary Janet Yellen.
Yellen announced in January that the country was in danger of reaching its limit.
McCarthy then said Congress would not increase the limit without an agreement from the White House to cut spending. Biden said he would not negotiate over lifting the limit because that would put the full faith and credit of the United States at risk.
The impasse was broken in late April when the House passed the Limit, Save, Grow Act, authorizing a $1.5 trillion increase in borrowing along with spending cuts and other measures favored by Republicans.
Biden then agreed to negotiate with McCarthy, resulting in the Fiscal Responsibility Act.
Opposition
A vocal minority of lawmakers in both parties opposed the bill.
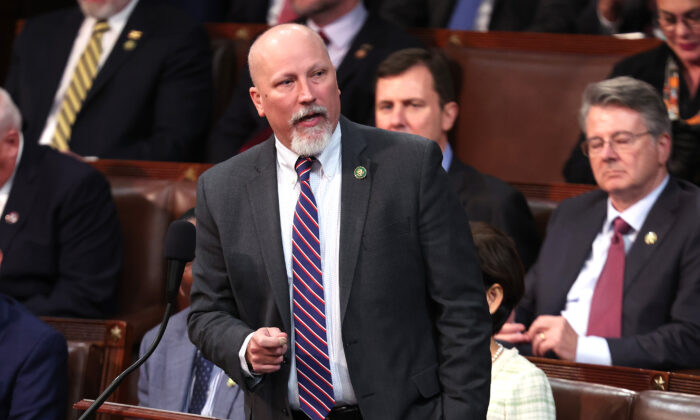
Some Republicans believed the agreement conceded too much to Democrats. Rep. Chip Roy (R-Texas) nearly blocked the bill in committee, but it cleared by a single vote.
Some Democrats opposed the agreement because it cuts discretionary spending and changes work requirements for the Supplemental Nutrition Assistance Program (SNAP). They said those provisions would hurt working Americans and those in need.

A group of Senate Republicans led by Lindsey Graham (R-N.C.) and Susan Collins (R-Maine) initially opposed the bill due to concerns about the level of defense spending. They were brought on board by assurances from Schumer and McConnell that emergency defense appropriations could be added later if needed.
The bill passed the House by a vote of 314 to 117 on May 31. Forty-six Democrats and 71 Republicans voted no.
The Senate passed the measure 63 to 36 the next day. Four Democrats, one Independent, and 41 Republicans voted no.
Mixed Reactions
Outside the Capitol, some observers applauded the bipartisan effort while others echoed the complaints of congressional dissenters.
“This kind of compromise is exactly how divided government should work,” Kelly Veney Darnell, interim CEO of the Bipartisan Policy Center, said in a June 2 statement.
EJ Antoni, a research fellow at The Heritage Institute, said “conservatives have little to celebrate with this deal, and much about which to complain.” According to Antoni, the bill doesn’t actually cut spending. He called it “left-wing legislation” in a statement published June 1.
Navin Nayak, counselor at the Center for American Progress, endorsed the legislation unenthusiastically, saying it was imperfect but necessary in a May 31 statement. Nayak said the Mountain Valley Pipeline, green-lighted by the bill, puts the safety of thousands at risk and the added work requirements will increase hunger in America.
Congress must now work the provisions of the Fiscal Responsibility Act into a federal budget and the dozen appropriations bills required to fund the government in the coming year.
The 2024 fiscal year begins on Oct. 1.
Jackson Richman contributed to this report.